As the name implies, the source of light in LED lamps are miniature electronic devices - LEDs. In conventional incandescent lamps, light is emitted by a red-hot metal spiral. In energy-saving lamps, light is emitted by a phosphor, which is deposited on the inner surface of a glass tube. In turn, the phosphor glows under the influence of a gas discharge.
Before moving on to the actual LED lamps, briefly consider the features of each type of lamp.
 Author photo
Author photo
Incandescent lamp it is very simple: a spiral made of refractory metal is fixed inside a transparent glass bulb, from which air is pumped out. Passing through a spiral, an electric current heats it to a high temperature, at which the metal glows brightly.
The advantage of such lamps is the low price. However, it is compensated by an equally low efficiency: less than 10% of the energy consumed by a light bulb turns into visible light. The rest is uselessly dissipated in the form of heat - the bulb heats up during operation. In addition, the service life of the device is very short and is approximately 1,000 hours.
Compact fluorescent lamp, or CFL (This is the exact name of an energy-saving lamp), at the same brightness, it consumes about five times less energy than an incandescent lamp. CFLs are more expensive and have several significant disadvantages for the consumer:
- quite a long time (several minutes) flare up after turning on,
- a lamp with its curved glass bulb looks unaesthetic,
- CFL light flickers, which is tiring for vision.
LED lamp represents several light-emitting diodes mounted in one case with the power supply unit. You can’t do without a power supply: for operation, the LEDs require DC power with a voltage of 6 or 12 V, in a household electrical network - AC with a voltage of 220 V.
 Author photo
Author photo
The lamp housing is most often made in the form of a familiar "pear" with a screw base. Thanks to this, LED lamps are easily installed in an ordinary lampholder.
Depending on the LEDs used, the color of the emission of LED lamps may be different. This is one of their advantages.
| Incandescent lamp | Energy saving | LED | |
| Emission color | Yellow | Warm day | Yellow, warm white, cold white |
| Power consumption | Big | Medium: 5 times less than incandescent bulbs | Low: 8 times less than incandescent bulbs |
| Life time | 1 thousand hours | 3-15 thousand hours | 25-30 thousand hours |
| disadvantages | Strong heat | Fragile, flare up for a long time | Low maximum power |
| Benefits | Low price, work in a wide range of conditions | Relatively economical and durable | Very economical and durable |
The advantages of LED lamps:
- very low power consumption - an average of eight times less than that of incandescent lamps of similar brightness,
- very long service life - they work 25-30 times longer than incandescent lamps,
- almost do not get warm,
- radiation color - to choose from,
- stable lighting brightness during fluctuations in the supply voltage.
The main advantage of LED lamps is efficiency. It is assumed that due to low power consumption and a long service life, LED lamps will significantly reduce lighting costs.
The price of LED lamps at the time of writing was about three times higher than that of conventional ones. Therefore, in monetary terms, they are 50-100 times more economical. Of course, this savings will be achieved provided that the lamp fully fulfills the promised service life and does not burn ahead of time.
The disadvantages of LED lamps limit their scope:
- uneven light distribution - a power supply built into the body obscures the light output,
- frosted bulb looks ugly in glass and crystal lamps,
- the brightness of the glow, as a rule, cannot be changed using a dimmer,
- unsuitable for use at very low (in frost) and high (in steam rooms, saunas) temperatures.
Emission color
Color is characterized by the color temperature, which is measured in kelvins: as the color temperature rises, the light changes from yellow to blue. In most cases, the color of the radiation is indicated on the package and lamp housing in degrees and the words:
- warm (2 700 K) - approximately corresponds to the emission of an incandescent lamp,
- warm white (3 000 K) - considered optimal for residential premises,
- cold white (4000 K) - for offices and industrial premises, close to daylight.
There are lamps with a variable color: when switching the mode, the emission spectrum of such a lamp changes.
It must be borne in mind that many people have a poor perception of the blue part of the spectrum, so the cold light of the lamps will seem dim to them. So, if you decide to install lamps with a cold spectrum in your home, choose them with a power margin.
Power
On the packaging of LED lamps, their luminous flux and power of incandescent lamps similar in brightness are indicated. The actual power consumption of LED lamps is on average 6-8 times less. For example, a 12-watt LED lamp shines as bright as a regular 100-watt bulb. This ratio can be used when selecting an LED lamp to replace an incandescent lamp.
However, an unpleasant surprise may lie in wait for you: the declared power may not correspond to the actual one, and the lamp will shine weaker than expected.
In addition, over time, the brightness of the LEDs decreases. It is possible that the light bulb will have to be changed long before the end of its life due to the fact that it began to shine too weakly.
Other important points
- Dimensions LED lamps are slightly larger in size than similar incandescent lamps. Therefore, in small plafonds they may not fit elementarily.
- If your lamp is turned on through a dimmer, you need the appropriate light bulbs. The packaging should indicate that the lamp is adjustable.
- The color rendering index of LED lamps is small: this means that they somewhat distort the visual perception of colors. In some cases, for example when photographing with LED light, this can be important.
LED Switching Strategy
Potential savings should not make you lose your head. Do not rush to run to the store and buy bulbs at once for all the lamps in the house. It is advisable to be guided by two principles.
- Replace only lamps with high power - 60 W or more. The savings from replacing low-power lamps will be small, and the cost of a new lamp may not pay off.
- Replace the lamps in fixtures, the burning time of which during the day is longer: for example, in chandeliers in living rooms. It makes no sense to change the light bulb in some utility room, the light in which is lit from case to case and for a short while.
Do not expect that power consumption will decrease significantly.
The main consumers of electricity in everyday life are all kinds of heating devices: an iron, an electric kettle, a washing machine, and especially an electric stove. According to several people surveyed, the electricity bill after switching to LED lamps is reduced by about 15-25%.
Another tip: do not buy many lamps of the same brand at once, first take one or two for a sample. The fact is that lamps with the same color temperature from different manufacturers can differ greatly in emitted light. Suddenly, the spectrum of these particular lamps will be disagreeable to you? Better to try.
Conclusion
LED lamps, compared to traditional incandescent lamps, are a fundamentally new lighting solution.
A few years ago they were a very expensive technical novelty, but today their price is already comparable to the price of other types of lamps. As for the characteristics, then LED lamps are noticeably superior to previous lighting devices. The verdict is clear: the transition to LED lamps is justified.
How does she look
The classic LED lamp (sometimes called an LED lamp), like an incandescent lamp, has a pear-shaped shape. Most often, its base part is made of white metal-plastic, and the bulb is a matte hemisphere made of plastic. This type of LED lamp is available with E14 and E27 sockets, which are most in demand among the population.  The LED bulb can be of any shape and can be made to any standard base. For example:
The LED bulb can be of any shape and can be made to any standard base. For example:
- GU5.3 - for directional ceiling lights,
- G4 - for chandeliers and decorative lamps,
- G13 - to replace linear fluorescent lamps.
More than 90% of today's LED lamps are assembled on SMD LEDs, which are miniature in size and at the same time have high light output. In addition to them, on sale you can see the so-called filament lamps, which look very much like an ordinary incandescent bulb (LF). Even less common are bulbs in which the light source is made in the form of a COB matrix, filled with a phosphor layer. Nevertheless, in the future it is planned that they will seize the initiative in the production of LED lamps.
What the LED lamp consists of
Conventionally, any LED lamp can be represented in the form of components: a block with LEDs, a radiator, a light-diffusing cap, a driver block, and a base. Light source SMD-LEDs - are located on a PCB board, which is connected to a radiator through thermal paste (heat-conducting adhesive). Most LED lamps with 220 V function as a radiator body. It is made of aluminum coated with a thin layer of white plastic. Inside the case there is a driver board designed to convert an alternating voltage of a 220 volt network to a constant voltage. The magnitude of the output voltage depends on the number and circuitry of installed LEDs. The driver connects to the base with wires or through a connector. In order for the light from the bulb to be evenly distributed in all directions, the LEDs are covered with a diffusing bulb, which also serves as protection against mechanical damage.  Linear LED lamps of the T8 type are arranged in a similar way. They just have a different shape and size of the components. In cheap LED lamps with a base type E14 and E27, the driver unit may not be available. Instead, in the center of the board with LEDs, a primitive transformerless power supply is sealed, which does not have current and voltage stabilization. Many miniature LED lamps are assembled in the same way, since there is not enough space inside their case for installing the driver.
Linear LED lamps of the T8 type are arranged in a similar way. They just have a different shape and size of the components. In cheap LED lamps with a base type E14 and E27, the driver unit may not be available. Instead, in the center of the board with LEDs, a primitive transformerless power supply is sealed, which does not have current and voltage stabilization. Many miniature LED lamps are assembled in the same way, since there is not enough space inside their case for installing the driver.
The main advantages and disadvantages
The ever-growing demand for LED lamps indicates their clear superiority over other sources of artificial light. Indeed, if you look at their technical characteristics, it will become clear that fluorescent and spiral lamps lose LEDs in almost all respects. And this despite the fact that LED technology continues to improve and has not yet reached its peak. There are really many advantages to LED lamps:
- Relative light output already reaches 30% (theoretical maximum for LEDs is 40%). For luminescent light sources, this indicator is 15%, and for LN does not exceed 3%.
- Low power consumption (7–9 times less than LN).
- Service life from 10 thousand hours and above. The declared service life of the flax - 1 thousand hours.
- Resistance to mechanical damage and vibration.
- Instant on. Moreover, the number of switching does not affect the operation of the LEDs.
- The absence of harmful substances, which allows them to safely operate and dispose.
- The ability to produce bulbs of different capacities and with any shade of light (cold, neutral, warm). And in "smart" LED lamps, the color of light and its brightness can be set remotely using a smartphone.
- During operation, the diffuser practically does not heat up, and the base temperature does not exceed 85 ° C.
It is worth recognizing that LED lamps are not ideal, which means that they have certain disadvantages:
- Relatively high cost. Even taking into account the fact that over the past 2 years, prices for them have decreased by more than 2 times and equal to the prices for CFLs, many people out of habit continue to buy “gluttonous” flax. To make sure that the purchase of an LED lamp, from an economic point of view, is fully justified by conducting simple calculations, which are summarized in a separate article.
- Harmful flicker, invisible to the naked eye and leading to general fatigue and headaches. This disadvantage is inherent in cheap LED lamps, the driver of which does not have current stabilization.
- The need for a step-down converter, as a result of which the cost of the product increases and its reliability decreases.
- LED lamps connected through a backlit switch and when turned off may flicker or dimly. The problem is solved by replacing the circuit breaker or finalizing the wiring diagram.
- A high percentage of defects, especially among cheap LED lamps. This drawback is due to the accelerated pace of production of LED products and the lack of proper technical control at all stages of manufacturing.
The principle of operation and the arrangement of lamps.

LED lamp design.
An LED light source consists of several elements connected in one housing. This is a socle, driver, radiator, LED and a diffuser bulb.
- Base - an element that is screwed into the cartridge of a chandelier or other lamp. Most often, for home use, a screw base type E27 and E14 is produced. It is made of brass with a nickel anti-corrosion coating. For other needs, light sources with a pin base are available.
- Driver - an element that stabilizes the incoming voltage, converting alternating current to direct. It also provides power to the LED. The driver consists of microcircuits, a pulse transformer, capacitors. In low-cost LED products, the driver may not be available. Instead, a simple power supply is used that does not provide stabilization of current and voltage. Also, the driver is not installed in miniature bulbs due to lack of space inside the case.
- Radiator - an element that removes heat from the LEDs and provides them with optimal temperature conditions. Usually it forms the visible part of the body of the lighting device. The radiator can be made of various materials: from expensive ceramics to cheap plastic. Aluminum and composite materials occupy an average niche: they are quite budget-friendly and efficiently remove heat.
- Diffuser - transparent "cap" that helps distribute light in space. It is made in the form of a hemisphere for scattering light beams at a wide angle. Polycarbonate or plastic is used as the material. In addition, the diffuser prevents dust and moisture from entering the housing. To soften the sharpness of light and reduce the irritating effect on the eyes, this element is coated with a phosphor from the inside. This achieves a color temperature similar to natural light.
- LEDs - the main working element of the lamp. Due to the work of the diode, a glow appears.
The principle of operation of LED lamps is based on physical processes in semiconductors. The glow appears after the passage of an electric current through the interface between two semiconductors (n and p), in one of which negatively charged electrons should prevail, and in the other - positively charged ions.It is worth noting that these materials pass current only one way. When it passes into charge carriers, they recombine - electrons transfer to a different energy level. As a result, light radiation visible to the eye appears. In addition to the glow, heat is also generated, which is removed from the LED with a radiator.
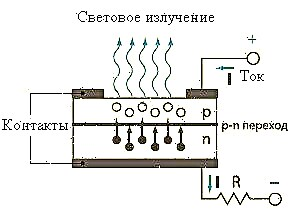
The appearance of optical radiation in the LED element.
At the dawn of appearance, LEDs could emit only a specific light wave: green, red or yellow. Therefore, LED elements were built into electrical circuits in the form of indicators. During the development of microelectronics, materials were found that made it possible to obtain a broad-spectrum light wave. However, this problem has not been completely resolved: either the blue wavelength or the red with yellow prevails in the glow of LED lamps. For this reason, they are divided into cold and warm, respectively.
Types and types of LED lamps.
There is no clear classification of LED lamps: the products are manufactured in too many different shapes, colors and configurations.
According to the method of application There are three types:
- General-purpose light sources for lighting apartments and offices. They are characterized by a scattering angle from 20 0 to 360 0.
- Products of directional light. These bulbs are called spots. They are used to create highlights or highlight interior areas in a room.
- Linear products similar to conventional fluorescent lamps. They are made in the form of tubes. They are used in technical rooms, offices, storerooms and in other spaces where fire safety is important. Create a bright, beautiful backlight that emphasizes the necessary details.
By type of destination LED lamps are divided into:
- Products for street use. They are made in dust and water resistant housing.
- Products for production purposes, utilities. Complemented with anti-vandal durable housing. They are made with special requirements for lighting characteristics: stability, service life, operating conditions.
- Household lamps. They are characterized by low power, stylish design, electrical and fire safety, the quality of the light flux (color rendering index, ripple coefficient, etc.).
Based power consumption Three types of lamps are also distinguished:
- With a power supply of 4 V. Low-power LEDs that consume from one to 4.5 V. They emit light of different wavelengths from infrared to ultraviolet.
- With a power supply of 12 V. This voltage is safe for humans, so these light sources are suitable for rooms with high humidity. Often available without a cap with pins, which complicates the connection process. An additional difficulty is the need for a special power supply, which will reduce the network voltage to 12 V. Convenient for use by motorists and tourists: they can organize lighting from the battery.
- With power supply 220 V. The most common type of product. Widely used for domestic use.
Why is LED lighting cool?
Why it was worth coming up with something better than “Ilyich’s bulbs” is understandable. They are dull, and warm, and beat, and shake. And why are LED lamps better than fluorescent "energy-saving" lamps? LEDs are often more expensive, but economical ones like both of them ...

No, even more economical. The brightness and power of the luminous flux, equivalent to the power consumption, LED lamps break records. When compared with an incandescent lamp - on average, LEDs are 10 times more economical. This means that a 100-watt incandescent lamp consumes 100 watts, shines equivalently to 100 watts and is heated like a small stove. The LED lamp, which will shine for about 100 watts, will consume only 10 and will hardly heat up.
When compared with fluorescent lamps, the difference is about 5 times in the direction of the benefits of LED lamps. That is, an energy saver that will produce light is equivalent to 100 watts, it will consume 20 watts. And the LED is still 10. In this material, we calculated in detail the efficiency of LED lamps and compared the costs of LED and CFL, respectively.
For LED lamps, the actual aperture is not always equal to the declared one. Some 10-watt lamps in terms of luminous flux will be lower than others. If accuracy is important to you, test the lamps yourself or study existing tests and calculations.
In addition to the material benefits, the small power of LED lamps also has a domestic advantage. Not every lamp or chandelier is able to withstand the high power of lamps - for chandeliers, sconces, table lamps, on average, the limit is 40-60 W per one ceiling, depending on the base. But a 40W LED lamp will shine like a 400-watt incandescent lamp. Therefore, here you are not limited in your choice: if it is dark for you, you can safely twist the lamp more powerful, without fear that your chandelier or lamp will burn out. With incandescent lamps this will not work: dark - endure.
Durability - Another bold plus towards LED lamps. While you change a dozen incandescent and several fluorescent lamps, the same LED lamp will continue to serve you faithfully. On average, their service life is from 5 to 10 years. In addition, many manufacturers and specialized stores provide a guarantee for any LED products from a year to three, so that your lamps can eventually become eternal. Efficiency, coupled with durability, quickly pay off the high cost of LED lighting.
If you experience irreconcilable nostalgia for incandescent lamps, among LED lamps there are filament ones - with transparent bulbs and LED rods that resemble incandescent filaments.
Reliability and ease of use. Only filament LED lamps cannot be shaken. Otherwise, from awkward falls, shaking, vibration, raising and lowering the ambient temperature (within the limits allowed by the manufacturer) LED lamps usually will not do anything.

Here you can add about environmental friendliness. For example, mercury is used in fluorescent spiral tubes. It is dangerous to break them, and after failure they must be disposed of at special collection points. If you accidentally broke an LED lamp, only fragments of the bulb will be from the dangerous one. During operation, it will not explode, as sometimes happens with incandescent lamps. Halogen lamps for spotlights can not be touched with your bare hands - they burn out very quickly from this. LED, as you already understood, no difference.
Are there any downsides? LED lamps do not really like the presence of a dimmer and a light indicator in the switches. For a dimmer (dimmer), you need to purchase special dimmable lamps. With indicators, the situation is simpler - modern switches, as a rule, no longer conflict with LED lamps. In older models, you can easily disconnect the indicator. Otherwise, the lamps will start to flicker, even when turned off, blink and quickly fail.
Colour temperature

Any LEDs come in three basic color temperatures with a bunch of midtones: warm, neutral white and cool white light. The description is always indicated by marking in degrees Kelvin.
Warm light. An excellent solution for retro-lovers who are sure that there is nothing better than a cozy light from an incandescent lamp. The light is noticeably yellow. In some cases, it really adds pleasant coziness and a feeling of warmth, in other situations it can distort the shades in the interior.
Fit: for interiors in warm colors: green, peach, wood, beige, etc. For bedrooms, offices, relaxation areas.
Not suitable: for interiors in cold colors - blue, blue, gray, white, black, lilac, cold pink, red, purple, etc. Do not use it in rooms where neutral lighting is important: dressing rooms, bathrooms, work areas.

Neutral white. Clean lighting with virtually no distortion, which is ideal everywhere. Neutral white does not affect the interior and does not add anything except light. In most cases, if you are not sure whether a warm or cold lamp is suitable for you, take a neutral white one and you will not lose it. This is especially an excellent solution for all rooms where accurate “color rendition” of space is important - where you most often look in the mirror, work, try on clothes, etc.
For different manufacturers, the “purity” and shades of color temperature may vary. 2700K warm light bulbs from one and the other brand can turn yellow in completely different ways. Therefore, it is better to select lamps of a single brand in one chandelier or one room.
Cold white. It is also called the "operating room light" because of the characteristic bluish glow. Cold white visually seems brighter, but this is only an optical effect. May make the room less comfortable. It is usually not recommended to put cold lamps in living spaces, leaving them for bathrooms, hallways, storage rooms. But use it carefully in the bathroom - an already not too comfortable room can become completely unfriendly.
Fit: for the interior in cold colors - all shades of blue, gray, black, purple, purple, cool pink. Non-residential premises.
Not suitable: for bedrooms, nurseries, interiors in warm colors. Caution in bathrooms and living rooms.

How many light bulbs to take?
The simplest formula for calculating the illumination, with which you definitely will not have problems: 20-30 watts of specific power per 1 square meter of the room. That is, for a room of 15 m², a total of 450 watts of light is needed. What does it mean? If you take, for example, a chandelier for five shades, each of them should give out about 90 watts. That is, we need five 9-watt LED lamps and it will be light and good. There is also a more complex calculation scheme based on the standards of illumination, light output, errors on the types of lighting devices, ceiling height, purpose of the room, etc.

Of course, any of the formulas has errors. First of all, individual preferences. Someone likes the room to be flooded with very bright light, someone likes tube muffling.
The specifics of the room also matter. For example, in the bedrooms some lack of light will be quite appropriate, because this is a relaxation room. In the kitchen, the light should not be just the norm, but better with a zoned distribution. But in the bathroom you can take it even in excess of the norm, since there are a lot of “blind spots” that absorb light, and with a lack of light the bathroom looks extremely uncomfortable.
Even if you like dim lighting - it is better to choose the number and power of the fixtures according to the standards, but add auxiliary lighting and make separate control. Then you will have a choice: turn down the light or make it brighter.
And finally, the most important thing is the logic of space. You must understand that no chandelier in the amount of one thing is able to efficiently illuminate a room of 25-30 squares or more or a long corridor. The light rays of the lamps simply do not reach in all directions. And even if you screw in the most powerful lamps that you find, you will be able to torture rather than a bright and comfortable room, because the light of this chandelier will mercilessly strike your eyes. What to do in this case? Fortunately, not only chandeliers are one. See, for example, how the zone lighting of a spacious room is distributed in the photo below.

Additional lighting
Additional lighting devices help to illuminate all areas of the room evenly and distribute light depending on the purpose. Some types - for example, panels or spotlights - can also act as the main light in certain cases.
Led panels

There are a variety of shapes, power and color temperature: round, square, elongated “tubes”, with and without a diffuser, built-in and overhead. The degree of dispersion depends on the case: transparent glasses do not disperse well, they hit pointwise, frosted ones disperse better. But in any case, the light panel is a concentrated beam of light with low scattering.
In a living room under such panels it may not be very convenient - you will constantly be struck by sharp, hard light in your eyes, most likely with impressive power. Led panels and overhead lights are good for technical rooms: bathroom, hallway, pantry, dressing room, offices and public places, etc. Great for additional lighting of work areas.
Due to the large amount of furniture in the kitchen, almost always one chandelier is not enough. In addition, when you face the kitchen set, you block your light with your back. Dots over the headset, LED overhead lights on an apron under the cabinets - you can still have a sconce in the dining corner for evening intimate tea parties, there will not be enough!
The downside of any ready-made panels and fixtures is that when they burn out, you will either have to solder the burned-out diodes on your own, or buy a completely new lamp. If the model is an invoice, there is no problem, but with built-in ones you will have to select according to the format of the slotted slot.
Spotlights

These babies are good at supporting basic lighting in living rooms. For example, if you have a large living room and one chandelier is not enough - put points around the perimeter and it will be light and bright. And with separate controls, it’s also convenient to adjust the amount of light according to your mood. Points often act as the main light in small rooms - bathrooms, hallways.
It is difficult to completely illuminate a large room with dots, because they are calculated on average one lamp per square meter. With LED lamps, they can shine quite brightly, equivalent to 90 watts of incandescent light, the rays on the ceiling will be clear and sparkling in contrast to halogen lamps, which give a blurry and dim glow.
Do not put spotlights in areas where you are most often and relax: over beds, sofas. Or consider the ability to turn them off separately. The light from spotlights is directional enough and can put pressure on your eyes if you decide to relax.
LED Strip Light

This little thing can do a lot and more. From highlighting the steps on the stairs to playing the role of a garland on a Christmas tree. Contour lighting of floors, ceilings, arches, additional highlighting of showcase and exhibition areas, workplaces: shelves, stands, kitchen sets, etc. LED strip varies in power, color temperature and its capabilities. Colored RGB-tapes on the control panel generally play in several colors, can shimmer, blink - beauty, and more. There are more budget tapes with open diodes, and there are tapes in silicone - it protects diodes from damage, and softens the glow, adding a light diffusion. There are tapes with protection against moisture, open splashes, dust.
Floodlights
Floodlights are both outdoor and indoor. Everything is clear with the street ones - a powerful long-range “flashlight” that will help you not to drown in the darkness of the night of your house territory or production. With internal more interesting. Usually they are used either in stores as the upper illumination of shop windows and stands, or in rooms with tall ceilings, where the range of ordinary lamps is not enough. Most often, the floodlights are rotary and are mounted up to several pieces on the railing - you can change their location.
Use extreme caution when using floodlights in low ceiling or small square living areas. These kids will give such a concentrated and directed light that you are unlikely to be comfortable under it.
Selection by technical parameters
Choosing an LED lamp in an apartment or a house must begin with technical specifications. This incandescent lamp had only power, and even the size of the cap.

LED lamp consists of several devices
LED lamps are more serious equipment, in addition to a crystal that emits light, there is also a built-in voltage converter - a driver that transforms an alternating mains voltage into 12 volts DC. So for the right choice you will have to familiarize yourself with some technical nuances.
Color rendering
Having lamps of the same color temperature, we can get a different perception of color. It depends on the color accuracy, which is characterized by the color rendering index (coefficient). It is denoted by the Latin letters CRI (Color Rendering Index), followed by numbers from 0 to 100. Sometimes indicated as Ra.
| Color Performance | Degree of color rendering | CRI color rendering ratio | Lamp examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Very good | 1 A | More than 90 | LED and halogen lamps, Philips TL-D 90 Graphica Pro, OSRAM DE LUXE and Color proof fluorescent lamps |
| Very good | 1 B | 80-89 | LED and fluorescent lamps (OSRAM LUMILUX, VANTEX, LDC, LBTC) |
| Good | 2 A | 70-79 | OSRAM BASIC fluorescent tubes |
| Good | 2 B | 60-69 | Fluorescent lamps LD, LB |
| Ample | 3 | 40-59 | Mercury lamps |
| Low | 4 | 39 and less | Sodium |
The highest value is 100. A light source with such a color rendering coefficient does not distort colors at all, but the cost of such a lamp will be very high. Lamps with CRI from 80 and above are considered normal for home lighting. It is in this range that it is worth looking for LED lamps for lighting a house. And again, you have to choose depending on the purpose of the lamp. For example, for illumination of paintings, it is advisable to use lamps with a color rendering coefficient of 100 or so, since they will not distort colors. For other rooms it is possible with lower rates.
Dispersion angle
A distinctive feature of LEDs is that they shine directly in front of you. A very small number of light waves are deflected to the sides. That is, the crystal itself produces a narrow beam of light. But the LED lamp contains some of these crystals. The light scattering angle depends on how they are located. This allows you to create a very narrow stream of light, and very wide. The scattering angle of LED lamps can be from 30 ° to 360 °.

It’s easier to understand what the light scattering angle is.
It is also necessary to choose the scattering angle of the LED lamp based on the purpose of the lamp. If this is a general lighting lamp located on the ceiling, the dispersion angle should be taken from 90 ° or more - up to 180 degrees. If it is a lamp for reading or for lighting some small area (for illumination of paintings, for example), it is worth choosing a more narrow beam.
In decorative luminaires with slots, it is worthwhile to put a lamp with a scattering angle of 360 ° or install narrowly oriented ones. You can get a very interesting effect.

Examples of using LED lamps with different scattering angles
If you have not been able to create a similar game of shadows before, now you know that you need to choose the right LED lamp.
Base type and radiator availability
The base is selected simply: under the available lamp. The industry produces LED lamps with standard bulbs for replacing incandescent bulbs (E14, E 27, E40), there are options for replacing halogen lamps (G4, GU5.3, GU10). There are LED lamps that are built into the furniture - to illuminate cabinets and cabinets. They have a base type GX53.

Table of image of socles and their names
One of the disadvantages of LEDs is that they heat up, and with a significant increase in temperature, they lose their brightness. With severe overheating, they can generally fail. There are two designs of LED lamps - in the form of a bulb familiar to us and without it - the so-called corn lamp. To better remove heat from crystals in bulb lamps, radiators are usually installed. In corn, due to the absence of a bulb, heat is removed efficiently and without a radiator.
There are several types of radiators for LED bulbs with bulb:
- Ribbed aluminum. It copes well with heat dissipation due to the ribbing, which increases the heat transfer area. But aluminum conducts current well to protect it from dangerous contact, the surface of the radiator is usually covered with paint or varnish.

Finned aluminum radiator is easy to distinguish

Smooth aluminum heatsink for LED lamps with varnish or paint

Ceramics remove heat most efficiently

Composite - medium and low price range
Choose a cheap LED lamp and hope that a ceramic radiator is installed in it is not worth it. But also get scared of plastic coolers too. They have more than a decent life and will repeatedly “beat off” the money spent on their purchase.
Lamps with ceramic or corrugated aluminum radiators should be installed in those places where heat dissipation is critical. For example, in built-in fixtures, in which the hottest back of the lamp is at the level of a stretch ceiling or furniture panel / wood / fiberboard. Here, strong heating can lead to changes in the structure and color of the material, which is clearly not good. In less critical situations, even plastic and composite radiators work normally - LED lamps still warm at times less than incandescent lamps.
Service life and warranty period
One of the most important parameters for consumers is a working resource. It is indicated in hours and shows how long the LED lamp remains operational (under normal operating conditions). The average “life expectancy” of modern LED lamps is about 30,000 hours, which is equivalent to 10 years, the maximum - of the order of 50-60 thousand - is about 15-18 years. But LED technology is actively developing and, most likely, LED lamps with a working life of 100,000 hours or even more will appear in the near future.

The data is very different
But do not flatter yourself. The working life is the time that a crystal is capable of emitting light. Unfortunately, there is such a thing as LED burnout. As a result of this phenomenon, they lose the brightness of the glow. The speed of these changes depends on the operating conditions - the less the LED overheats and the less it is at low temperatures, the longer the initial brightness is maintained. How to understand how long the lamp will last without loss of brightness? According to the warranty period of operation. This figure more realistically reflects the state of affairs, since in case of problems the device is simply replaced with a new one. Here, on the contrary, manufacturers are inclined to slightly underestimate the figure so that there are as few warranty cases as possible.
Dimming
You can change the brightness of the lighting in the room in two ways - by increasing or decreasing the number of lighting devices turned on or by setting the brightness control - dimmer. The second method is more convenient, since it allows you to precisely “adjust” the lighting to the requirements by gradually changing the brightness of the glow by turning the knob.

To select an LED lamp for connection with a dimmer, look for the dimming limit in the characteristics
But, if you need to choose an LED lamp in a network with a dimmer, there should be a note in the technical specifications that it is dimmable. Normal will shine at full strength, and at a certain position of the dimmer just starts to blink.
In addition to the fact that the lamp must be dimmable, it is necessary to look at the dimming limit. For some, the minimum dimming limit is 5%, for others - 20%.
Manufacturers rating
Choosing an LED lamp according to its technical parameters is not all. You will have to decide on the manufacturer. In light of the fact that LED lamps are not so cheap, I want to save and buy from those that are cheaper. These are, as a rule, Chinese lighting fixtures, moreover, that does not differ at least in normal quality. Their distinguishing feature is poor packaging, lack of a warranty period, or it is, but very small. They are assembled mainly from the cheapest parts, as a result, the color rendering coefficient (real, not written) can not exceed 60, due to poor-quality parts in the lamp converter, it flickers. It's hard to talk about the life of such products - here's how lucky. In general, no matter how much you would like to save, it is better to choose an LED lamp from the products of normal manufacturers.
The highest quality
Very good products are produced by European companies Philips and Osram. Their offices are in Europe, but the factories are mainly located in China. Despite this, they produce LED lamps of very good quality. The image must be maintained, because quality is strictly controlled. This is so, but their prices are high. Philips LED lamps cost from 800 to 1800 rubles apiece, Osram has budget lines with a cost of 100 rubles, there is a premium with a price of 2700 rubles, and the average range is from 400 to 800 rubles.
Normal quality at a low price
The best combination of price and quality can be found among representatives of the middle price category. There are Russian manufacturers, there are Chinese, some other Asian countries are also represented. The products of these firms have predominantly good product ratings. Also, the declared data coincides with the realities:
- Russian company Feron (Feron). One of the areas of activity is the production of lighting devices based on LEDs. Prices from 60 rubles for low-power built-in, up to 360 rubles.
- Camelion (Camelion). The campaign from Hong Kong produces several lines with different caps. Prices from 75 rubles to 400.
- St. Petersburg company Jazzway (Jazzway). It produces LED lamps with various caps, bulb and tube. The price range is about the same - from 100 to 370 rubles for normal power lamps (up to 20 watts), there are powerful (30-60 watts) their price - from 3700 to 6700 rubles.
- Another Russian company Gauss (Gauss) is considered the leader of this market among domestic manufacturers. Prices - from 83 rubles for rulers with not the best characteristics, up to 1600 rubles for super-economical.

Choosing an LED lamp from such a variety is not easy
There are many other companies, but reviews of the products of these companies are often negative. If you want to choose a good quality LED lamp for the sane money - take a look at the above brands.



